ENG phonetics
06 Jun 2018 • Leave CommentsReferences
- BBC pronunciation
- english phonology
- iowa phonetics
- Cambrige: an international pronunciation course
- American Accent Training
- https://v.qq.com/x/page/w0146n8467c.html
Tips
-
Open Open Open your mouth;
It means not only begin to practice, but keep your mouth and tongue movement to certain extent, speaking loud.
- Check dictionary.
- Film and TV series are not a proper guide. Use standard prounciation materials.
- Improve intonation.
IPA
The International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) is an alphabetic system of phonetic notation based primarily on the Latin alphabet.
The IPA is designed to represent only those qualities of speech that are part of oral language: phones, phonemes, intonation and the separation of words and syllables.
IPA symbols are composed of one or more elements of two basic types, letters and diacritics (变音符号). English letter ⟨t⟩ may be transcribed in IPA with a single letter, [t], or with a letter plus diacritics, [t̺ʰ], depending on how precise one wishes to be. Often, slashes are used to signal broad (宽式注音) or phonemic transcription (音位注音,也称严式注音); thus, /t/ is less specific than, and could refer to, either [t̺ʰ] or [t], depending on the context and language.
1888 年 8 月第一套国际音标符号诞生,这套符号设立的原则是:每一个独立的音都有一个独立的符号相对应,相同的符号在任何语言中都表示同一个发音。
发音过程
- 气流 airstream: 从肺部出来;
- 发声 phonation: 喉部(声带)决定清音和浊音;
- 口鼻 oro-nasal: 气流进入口腔还是鼻腔,形成鼻音和口腔音;
- 发音 articulation: 通过舌的运动改变口腔的形状,发出各种不同的口腔音。
结合这四个步骤,我们可以对发音进行不同的分类。
Vowel vs. Consonant
语音一般分为辅音 (consonant) 和元音 (vowel) 两大类,元音和辅音的根本区别在于气流是否受阻。注意是“受阻”不是“完全没有”。发辅音时,声道紧闭或声道变窄使气流无法排出,或排出时会产生能够辨别出的摩擦。发元音时气流可以相对不受阻碍地从口腔或鼻腔中排出而不会产生类似的现象。
A vowel is a sound such as the ones represented in writing by the letters 'a', 'e' 'i', 'o' and 'u', which you pronounce with your mouth open, allowing the air to flow through it.
A consonant is a sound such as 'p', 'f', 'n', or 't' which you pronounce by stopping the air flowing freely through your mouth.
因此,在描述辅音音姿的时候,特别需要考虑的是气流在口腔中受阻的位置和方式,而描述元音时,需要考虑的主要是舌在口腔中的位置。
从理论上讲,一个音段要么是元音,要么就是辅音。但像 yet 中的 [j] 和 wet 中的 [w] 实际上是完完全全的元音,只是它们出现在辅音的位置上。我们一般用术语“半元音 (semi-vowel)”来描述这些既非元音又非辅音,而是处于中间状态的语音。
We can also divide phonation into voiceless (清音:声带不颤动) and voiced (浊音:声带颤动)。对应的我们有“清辅音”和“浊辅音”。对于元音,所有的都是“浊元音”。我们还可以根据是否“送气(aspirated)”来区分发音,如在 peak 中 /p/ 送气,用 [pͪ] 表示,在 speak 中 /p/ 不送气,用 [p] 表示。peak 的严式注音为 [pͪik], 宽式注音为 [pik], 严式注音包括了对送气现象的表述。
长短元音符号
英语词 fit 和 feet 中间的元音是用长度符号 [ː] 来区分的(即 fit [fit], feet [fiːt]),表示为 [iː, i; uː, u; ɔː, ɔ; ɜː, ɜ]. 现在有了独立的短音符号 [i, ɪ; u, ʊ; ɔ, ɒ; ɜ, ə],每一对的前者是短音,后者是长音。有字典为了便于区别,同时标注长度符号和新短音符号 [iː, ɪ; uː, ʊ; ɔː, ɒ; ɜː, ə].
Syllable 音节
元音和辅音都是指的单个发音,称为“音段(segment)”,当音段组合成音节(syllable)。通常把音节分成两个部分:韵基(rime)和节首(onset), 韵基中的元音是节核(nucleus), 后面的辅音称作节尾(coda)。
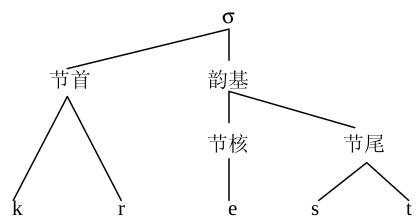
所有音节必须有节核,但不是所有的音节都有节首和节尾。没有节尾的音节叫做“开音节(open syllable)”, 有节尾的音节叫做“闭音节(closed syllable)”。
在词的层面上,一个词在单独提及的时候(即单词本身没有在句子里)称为“引用形式(citation form)”,这时至少有一个音节是重读的。也就是说,如果某个词是单音节词,那么这个词的引用形式必须是重读的,如不定冠词 a,单独说这个词的时候应该说 [eɪ],而不是 [ə]. 虚词一般都有重读和轻读两种形式,在短语和句子的层面上一般采取轻读。
在多音节的词中,至少有一个音节是重读音节。在比较长的词中(一般指 4 个音节以上),还会有两个重读音节。